Contents
Audio Podcast on Retirement Planning
Defining Your Financial Future
Retirement – it’s a phase of life many look forward to, envisioning freedom, travel, and time for passions. But achieving a comfortable and secure retirement doesn’t just happen; it requires foresight and deliberate action. This is the core concept of retirement planning: a proactive, lifelong process of setting financial goals for your post-work years and developing a strategy to achieve them.
Whether you’re just starting your career or are decades into it, understanding retirement planning is crucial. It might seem complex with its own retirement planning lingo (Link to Pillar 1.4), but at its heart, it’s about taking control of your financial destiny. This comprehensive guide will break down what retirement planning truly involves, why it’s absolutely essential, the key components you need to understand, and how it impacts your life stages.
What Does Retirement Planning Actually Involve?
Retirement planning goes far beyond simply putting money aside. It’s a holistic process encompassing several key activities:
- Defining Your Vision: What do you want your retirement to look like? This involves considering lifestyle factors like where you’ll live, how you’ll spend your time (hobbies, travel, volunteering), and your desired standard of living. (Future Link to 1.3: Defining Your Initial Retirement Goals & Vision)
- Setting Financial Goals: Translating your vision into concrete, measurable financial targets. How much income will you need annually? What total savings amount does that imply?
- Consistent Saving: Developing the habit of regularly setting aside a portion of your income specifically for retirement. (Future Link to 1.13: Basic Budgeting Techniques)
- Strategic Investing: Making your savings work for you by investing them appropriately to outpace inflation and grow over the long term. (Future Link to 1.17: Introduction to Basic Investment Concepts)
- Managing Risk: Understanding and mitigating risks like market volatility, inflation, and outliving your savings (longevity risk).
- Income Generation Planning: Strategizing how you will convert your accumulated savings into a reliable income stream during your retirement years. (Future Link to Silo 4 Pillar Page)
It’s a long game, requiring discipline and periodic adjustments as your life and financial situation evolve.
Why Retirement Planning is Non-Negotiable
In today’s world, actively planning for retirement isn’t just advisable; it’s essential. Here’s why:
- Increased Longevity: People are living longer, meaning retirement could easily last 20, 30, or even 40 years. You need adequate funds to last potentially much longer than previous generations. Failing to plan for longevity is a primary risk of not planning.
- The Inflation Factor: The impact of inflation means your money loses purchasing power over time. Planning helps ensure your savings grow faster than rising costs.
- Rising Healthcare Costs: Healthcare is a massive and growing expense in retirement, often underestimated. Planning for healthcare costs (Link to Pillar 3.11) is critical.
- Decline of Traditional Pensions: Unlike past generations who could rely on the three-legged stool including hefty pensions, most workers today bear the primary responsibility for funding their retirement via personal savings. Relying solely on a pension, even if you have one, is risky.
- Social Security is Supplemental: While vital, Social Security benefits (Link to Pillar 3.6) are designed to supplement, not fully replace, pre-retirement income for most people.
- Achieving Your Goals: Planning is the roadmap to achieving the retirement lifestyle you envision, rather than leaving it to chance.
- Peace of Mind: Having a plan significantly reduces financial anxiety and provides a sense of control over your future. Explore the psychological benefits of planning (Link to 1.1.19).
The potential outcomes with early planning versus without it (Link to 1.1.21 / 1.1.22) are dramatically different.
Key Building Blocks of Your Retirement Plan
Several core components form the foundation of most retirement plans, especially early on:
- Retirement Accounts: Understanding and utilizing tax-advantaged accounts like employer-sponsored 401(k)s (Future Link to 1.7) and Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs – Traditional & Roth) (Future Link to 1.8, 1.9, 1.10) is fundamental. (Future Link to 1.6: Introduction to Different Retirement Account Types)
- Compound Interest: Recognizing this as the engine of long-term growth motivates early saving. (Future Link to 1.2: The Power of Compound Interest)
- Employer Match: Maximizing this “free money” is often the first crucial step. (Future Link to 1.11: The Importance of Employer Matching Contributions)
- Saving & Budgeting: Creating room in your current finances to save consistently. (Future Link to 1.13: Basic Budgeting Techniques)
- Basic Investing Principles: Understanding asset allocation, diversification, and risk tolerance. (Future Link to 1.17, 1.18)
- Goal Setting: Defining what you’re saving for. (Future Link to 1.3)
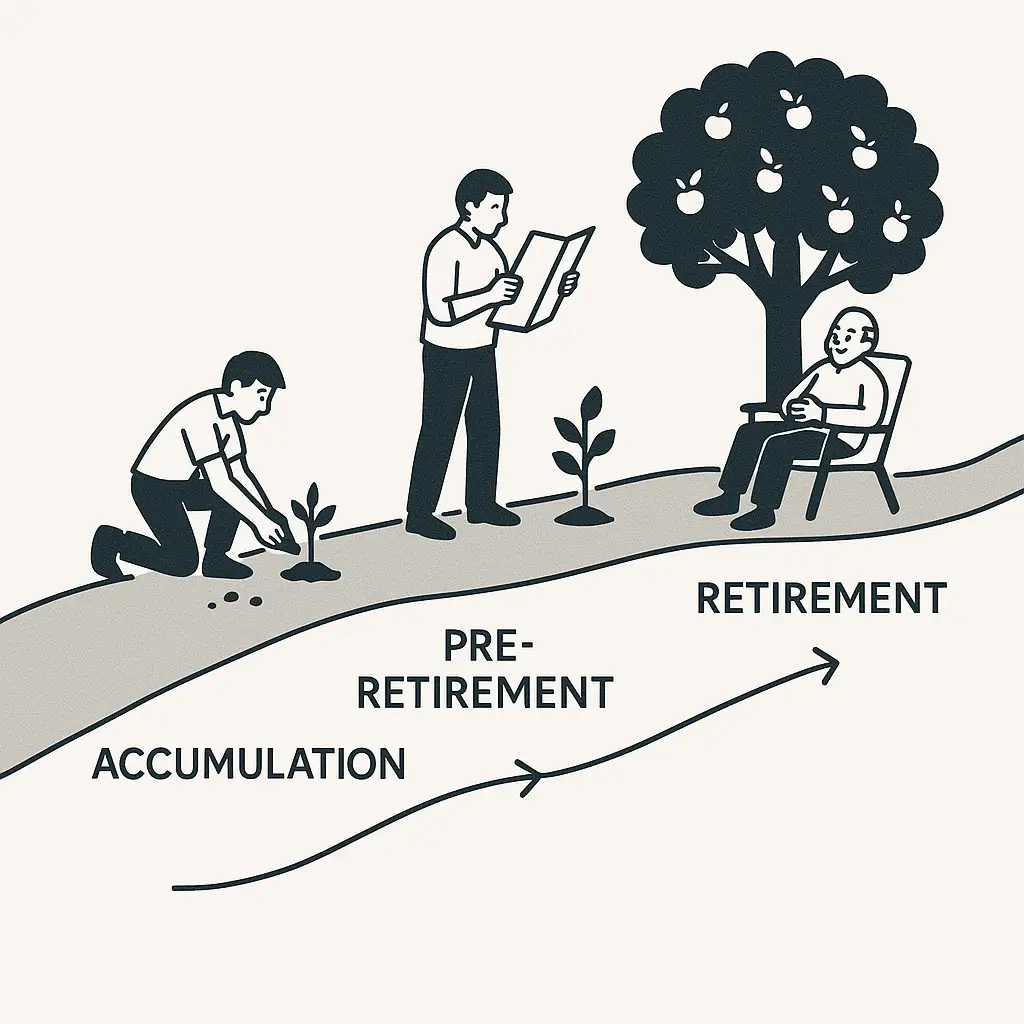
Retirement Planning Across Your Lifecycle
Your focus shifts throughout the stages of the retirement plan lifecycle (Link to 1.1.17):
- Accumulation (20s-40s): Focus on starting early, maximizing growth, and building habits. (Link to Silo 1 Pillar Page)
- Pre-Retirement (50s-60s): Accelerate savings, refine goals, make key decisions on income/healthcare. (Link to Silo 3 Pillar Page)
- Retirement/Decumulation (60s+): Manage income streams, make savings last, adjust for life changes. (Link to Silo 4 Pillar Page)
Understanding how planning impacts your current decisions (Link to 1.1.20) is key at every stage.
Modern Retirement: Beyond Stopping Work
It’s also important to recognize that retirement doesn’t always mean stopping work completely (Link to 1.1.18). Many pursue phased retirement, part-time work, or encore careers, adding another layer to planning. This ties into the concept of financial independence versus traditional retirement.
Getting Started: The Power of Now
The most critical takeaway? Starting now is more important than starting big. Don’t be intimidated by myths about needing millions or feel it’s too late to start (Future Link to 1.30). The journey begins with understanding these core concepts and taking the first step.
Explore Further:
- Dive deeper into different retirement account types (Future Link to 1.6).
- Learn about the incredible power of compound interest (Future Link to 1.2).
- Start defining your initial retirement goals (Future Link to 1.3).
- Understand how much you should realistically save (Future Link to 1.14/1.15).
Conclusion
The core concept of retirement planning is about intentional preparation for a secure and fulfilling future. It requires understanding your goals, leveraging time and compounding, utilizing the right tools (like retirement accounts), managing risks, and adapting throughout your life. By embracing planning today, you empower yourself to build the retirement you deserve.

👋 Hi, I’m Jaiveer Hooda, the content creator behind Grow Your Money Smart!
I’m passionate about exploring the world of personal finance and sharing actionable insights to help you manage debt, plan for a secure retirement, and create passive income streams. 💡 My goal is to simplify complex financial topics and empower you to make smarter money decisions.
Let’s grow your wealth together, one smart move at a time! 💸
16 thoughts on “What is Retirement Planning? Your Essential Guide to Securing Your Future”